Governments typically purchase the amount of the surplus or impose production restrictions in an attempt to reduce the surplus.
Do price floors create shortages or surpluses.
Price floor is enforced with an only intention of assisting producers.
Does a binding price floor cause a surplus or shortage.
On a graph of the supply and demand curves the supply and demand curve intersect at the equilibrium the point where the quantity.
A shortage or surplus occurs when the supply for a good or service does not equal demand with shortages causing a general rise in price and surpluses causing prices to fall.
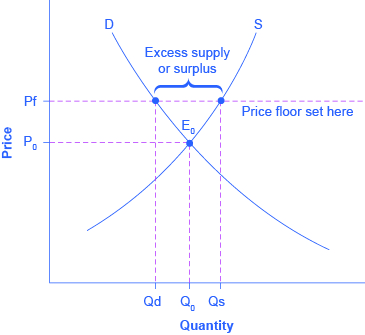
When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price quantity supplied will exceed quantity demanded and excess supply or surpluses will result.
In agriculture price floors have created persistent surpluses of a wide range of agricultural commodities.
Price floors prevent a price from falling below a certain level.
The price change continues until a new equilibrium between supply and demand is reached according to the experimental economics center from the andrew young school at.
When government laws regulate prices instead of letting market forces determine prices it is known as price control.
An example of a price ceiling we can use to explain the concept would be rent control.
Price floors prevent a price from falling below a certain level.
In this case it is a surplus of workers suppliers of labor more of whom are willing to work in minimum wage jobs than there are employers demanders willing to hire at that wage.
Imagine if you had to rent out the front apartment of the farm for half of what you wanted to rent because of some new law obama made.
Unfortunately it like any price floor creates a surplus.
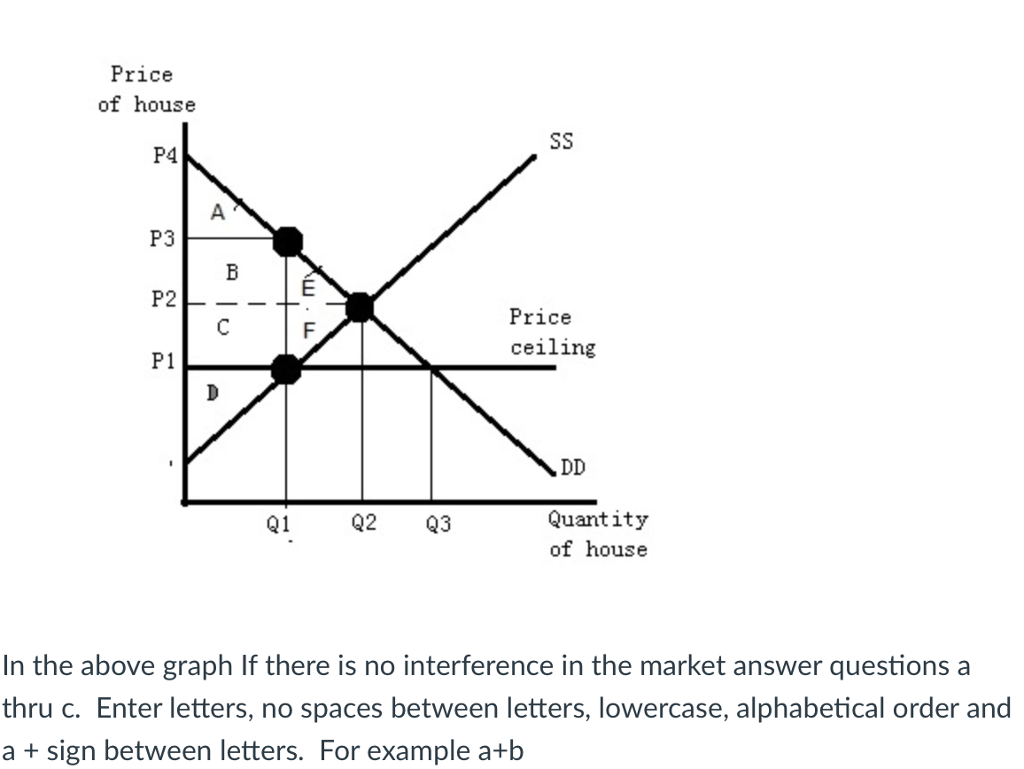
Price floors and price ceilings often lead to unintended consequences.
If price floor is less than market equilibrium price then it has no impact on the economy.
However price floor has some adverse effects on the market.
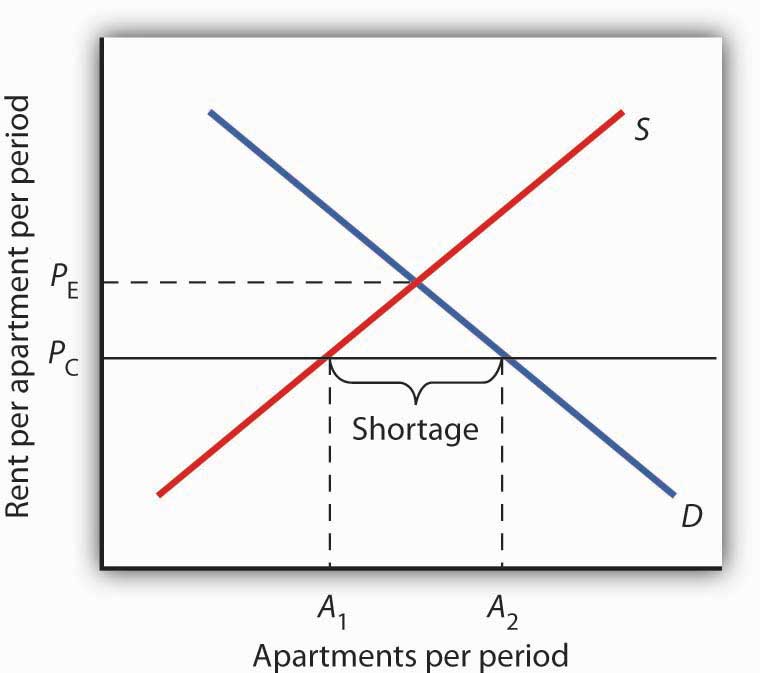
One way shortages occur is through a price ceiling.
After the establishment of the price floor the market does not clear and there is an excess supply of amount qs qd.
We call a surplus caused by the minimum wage unemployment.
Price ceilings create shortages by setting the price below the equilibrium.
How does consumer surplus and producer surplus change when a price control is imposed.
But if price floor is set above market equilibrium price immediate supply surplus can be observed.
Producers are better off as a result of the binding price floor if the higher price higher than equilibrium price makes up for the lower quantity sold.